Introduction
Research in the field of medicine is finding several cures for lethal diseases such as cancer, AIDS, hepatitis, and many others. Since the start of curative treatments, plants have been considered a vital source to produce medicines. One such controversial plant that has multiple benefits in the field of medicine is Cannabis Plant. Let us dive into the benefits of Cannabis Plants extracts and how it supports the natural mechanisms in our body.

Endocannabinoid System (ECS) And Its Key Pieces
The Endocannabinoid system has an essential role in homeostasis in our body, and this system is present throughout the animal kingdom. Although researchers have not been able to understand the complete function of ECS, yet it has been proved that it plays a part in regulating a wide range of processes and functions such as:
- Mood
- Appetite
- Memory
- Pain
- Reproduction and fertility
- Immune responses
- Gastrointestinal functions
The 3 Main Components Of The Human Endocannabiniod System Are:
- Cannabinoid Receptors

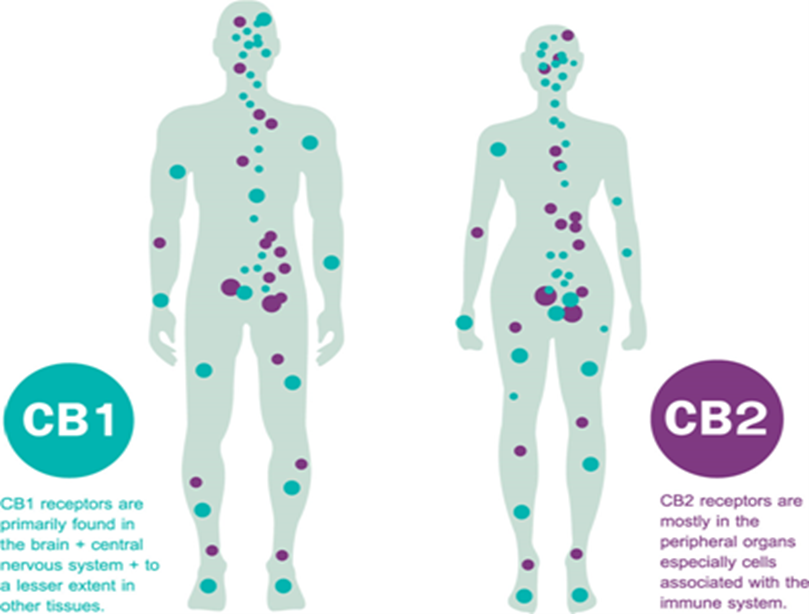
The ECS comprises two G-coupled receptors:
- CB1
- CB2
Plant-derived or exogenous (derived from outside the body) cannabinoids can interact with these two receptors. Endocannabinoids and their receptors are present throughout the body: in the brain, connective tissues, organs, glands, and immune cells, as shown in the diagram above. With their multiple actions in our immune system, nervous system, and virtually all body organs, the endocannabinoids act like a bridge between the mind and body.
These are the small molecules that help in activating the cannabinoid receptors. These are also known as endogenous cannabinoids as they are produced by the body internally and interact with their receptors to initiate specific bodily functions, as mentioned above.
The body itself produces its endogenous cannabinoids:
- anandamide
- 2-AG
Both of these endocannabinoids have a strong affinity with the ECS receptors: CB1 and CB2.
Metabolic Enzymes
The body has ways to regulate its functions. In ECS, the body has ways to generate, regulate and break down endocannabinoids when required. This is done with the help of two enzymes:
- FAAH breaks down anandamide.
- MAGL breaks down 2-AG.
These enzymes degrade the excess endocannabinoids to ensure regularity in the ECS.
CBD vs THC: Chemical structure
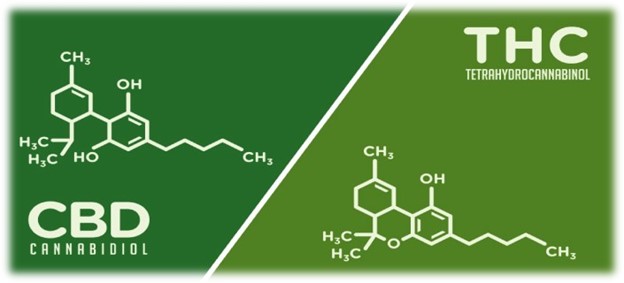
Both THC and CBD have the same molecular structure:
- 21 carbon atoms
- 30 hydrogen atoms and
- 2 oxygen atoms.
The only difference is the arrangement of atoms in each structure, which accounts for different body effects. Both the cannabinoids are similar to the body’s endocannabinoids which allows their interaction with the cannabinoid receptors. These interactions result in the release of neurotransmitters in the brain. Neurotransmitters are chemicals that relay messages between cells and function in the immune system, pain, stress, and sleep.
CBD vs THC: Side Effects
CBD is overall considered safe to consume and is tolerated even in a large number of doses. However, studies have shown that if any side-effect is reported with CBD consumption, it is because of its interaction with some other medication being taken simultaneously.
THC causes temporary side effects, which include:
- increased heart rate
- coordination problems
- dry mouth
- red eyes
- slower reaction times
- memory loss
- anxiety
CBD’s side effects may include:
- appetite changes
- fatigue
- weight loss
- dizziness
- diarrhoea
CBD And THC Interation With The Endocannabiniod System
Since the legalization of hemp and other cannabis extracts, consumers are eagerly waiting to try these natural extracts to cure the diseases which are not being treated with the conventional or the available medicines in the market. The two extracts found in plants of the Cannabis genus are:
• cannabidiol (CBD) and
• tetrahydrocannabinol (THC),
CBD is being consumed in the form of gummies, gels, oils, extracts, supplements and more. As opposed to CBD, THC is the main psychoactive compound that makes a person high. It is available in tinctures, edibles, oils, capsules, and more. Both compounds interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system, but they have quite different effects.
Plant cannabinoids have psychoactive and medicinal effects in the body because of the presence of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) with which these compounds can interact. A person who ingests THC gets high because of its interaction with the CB1 receptor present on the body cells. Scientists do not yet know the way CBD interacts with ECS. Still, it has been believed that CBD prevents the breakdown of anandamide by inactivating the enzyme FAAH, which breaks down anandamide. This causes more availability of anandamide, which means it can have more of an effect on the body. Therefore, CBD is indirectly facilitating the ECS by making more endocannabinoids available for certain functions.
Studies have proven that the inhibition of the FAAH enzyme can be an effective way to treat anxiety disorders. Many studies done in the lab, in-vitro and in-vivo, have proven that CBD is beneficial in treating cancer. Experiments conducted in mice confirmed that CBD inhibits the cancerous cell growths in the lungs and colon. No studies have been led in humans so far. However, people suffering from cancer tried CBD to treat the disease and saw improvement in their health. Such people had reduced symptoms of vomiting, depression and nausea.
Moreover, cannabinoids are often prescribed by doctors to those who are suffering from chronic pain, in the states where cannabis is legalized. Plant cannabinoids have also been used to treat epilepsy, pain, arthritis, nausea and depression for thousands of years. Medical research must be conducted to record the scientific evidence supporting this connection.
Conclusion
The Endocannabinoid system is yet to be fully understood by scientists and medical doctors to be able to cure multiple lethal diseases. Although the treatments using plant cannabinoids show promising results among patients suffering from cancer and other such diseases, much research and human studies needs to be conducted to strengthen the assumption and theoretical beliefs.
Further Reading
Introduction to Medical Cannabis
How and where to safely buy RSO medical cannabis oil online
References:
- Pacher, P., Kogan, N. M., & Mechoulam, R. (2020). Beyond THC and endocannabinoids. Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology, 60, 637-659.
- Silver, R. J. (2019). The endocannabinoid system of animals. Animals, 9(9), 686.
- Szaflarski, J. P., & Bebin, E. M. (2014). Cannabis, cannabidiol, and epilepsy—from receptors to clinical response. Epilepsy & Behavior, 41, 277-282.
- Guindon, J., & Hohmann, A. G. (2011). The endocannabinoid system and cancer: therapeutic implication. British journal of pharmacology, 163(7), 1447-1463.
- Guzmán, M. (2018). Cannabis for the management of cancer symptoms: THC Version 2.0?. Cannabis and cannabinoid research, 3(1), 117-119.
- Laezza, C., Pagano, C., Navarra, G., Pastorino, O., Proto, M. C., Fiore, D., … & Bifulco, M. (2020). The endocannabinoid system: A target for cancer treatment. International journal of molecular sciences, 21(3), 747.
- Abrams, D. I., & Guzman, M. (2015). Cannabis in cancer care. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 97(6), 575-586.
- Cristino, L., Bisogno, T., & Di Marzo, V. (2020). Cannabinoids and the expanded endocannabinoid system in neurological disorders. Nature Reviews Neurology, 16(1), 9-29.
- Kilaru, A., & Chapman, K. D. (2020). The endocannabinoid system. Essays in Biochemistry, 64(3), 485-499.
Help and Advice
If you need advice or help with Medical Cannabis, please use the contact form.
We try to answer all emails within 24 hours and are happy to help and provide advice on all aspects of Medical Cannabis treatments in complete confidence.
Disclaimer: Please note that whilst we consider ourselves subject matter experts regarding Medical Cannabis, we are not medically trained professionals. We are an information resource and there is still limited evidence that Medical Cannabis can cure all the illnesses we discuss here. We recommend you do as much research as possible, and where practical seek professional medical advice before proceeding with Medical Cannabis oil. In short, always do your homework.